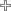Technical data
| Model | Connections | Motor power , kW |
| CTM 20-7 | 3/4" / 3/4" | 0.12 |
| CTM 25-8 | 1" / 1" | 0.25 |
| CTM 25-10 | 1" / 1" | 0.55-0.75 |
| CTM 32-12.5 | 1 1/4" / 1" | 0.75-1.1 |
| CTM 40-12.5 | 1 1/2" / 1 1/4" | 1.5-2.2 |
| CTM 50-12.5 | 2" / 1 1/2" | 3-4 |
Perfect choice for chemically corrosive and toxic liquids.
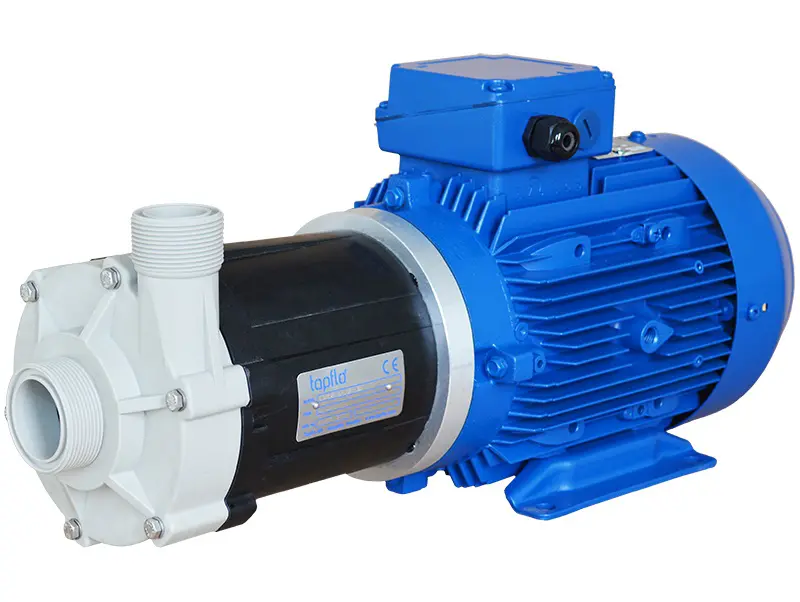
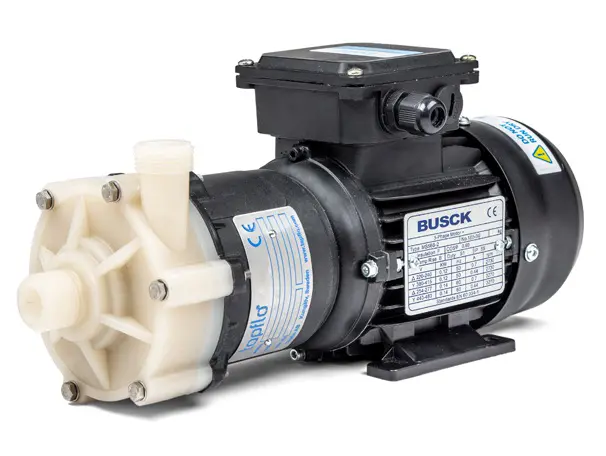
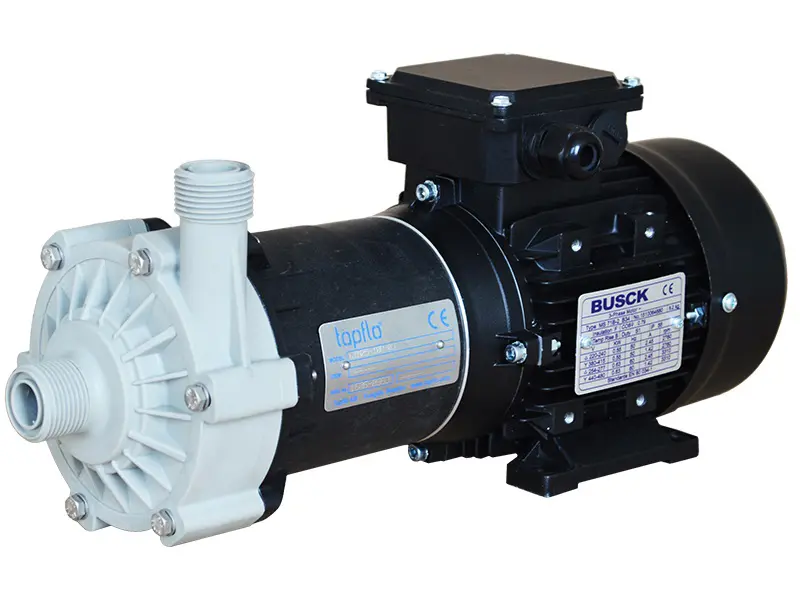
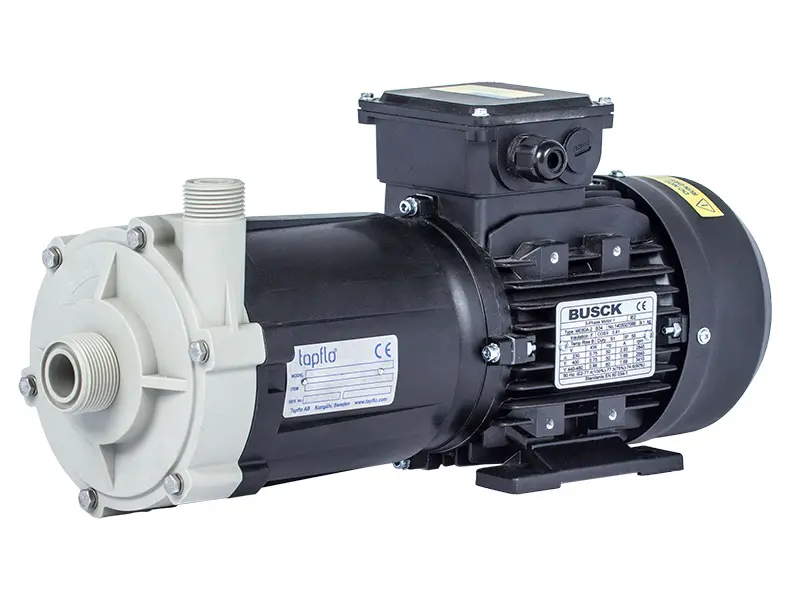
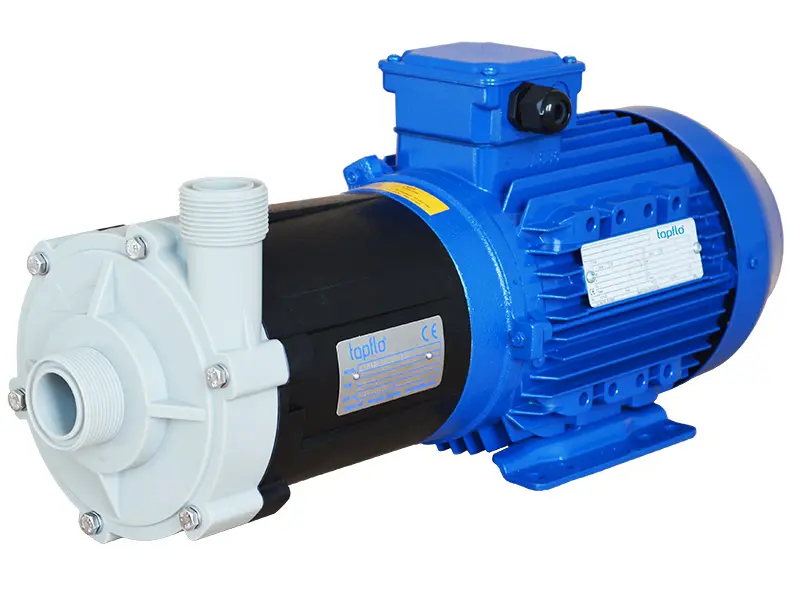
CTM is a compact close coupled pump perfect for service in little spaces like in OEM installations.
Tapflo CTM magnetic drive pumps are centrifugal pumps where the power from the motor is transmitted to the impeller by means of a magnetic coupling.
CTM pumps are designed and manufactured for transfer of chemicals and circulation in surface treatment industry
Features & Benefits
- No leakage
- Economical operation
- Magnetic power transmission
- Safe handling of hazardous fluids
- Hermetic system
Typical APPLICATIONS
- Transfer of chemicals
- Surface treatment
- Food and beverage
- Water treatment
- Chemical manufacture
- Demineralization
- Photo processing
- Liquid crystal manufacture